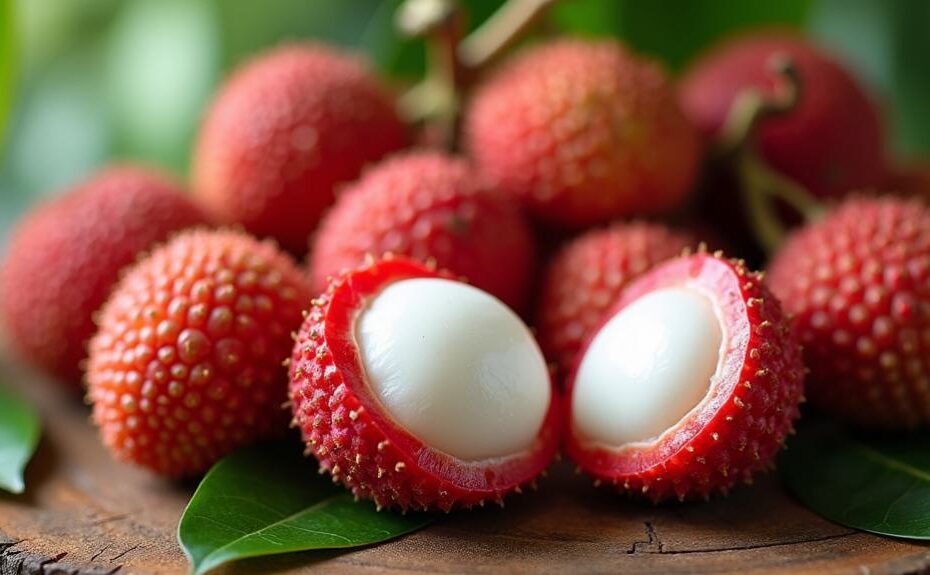
Lychee is a tropical fruit known for its sweet, floral flavor and vibrant pink skin. It boasts a wealth of nutrients, including an abundance of vitamin C, which is essential for immune support and skin health. Additionally, lychee contains various phytonutrients that may offer protective benefits against chronic diseases.
The nutritional profile of lychee, its health benefits, potential risks, and tips for incorporating it into your diet are explored in this post, below.
Trumpai
- Lychee is low in calories, with one cup providing about 125 calories and high water content for hydration.
- Rich in vitamin C, lychee supports immune function and provides over 100% of the daily value in a 100g serving.
- Contains essential minerals like copper and potassium, promoting heart health and red blood cell production.
- Antioxidants in lychee, including flavonoids and polyphenols, help combat oxidative stress and may reduce cancer risk.
- Unripe lychee can be toxic, causing hypoglycemic symptoms; allergic reactions may occur, requiring caution.
Nutritional Content Overview
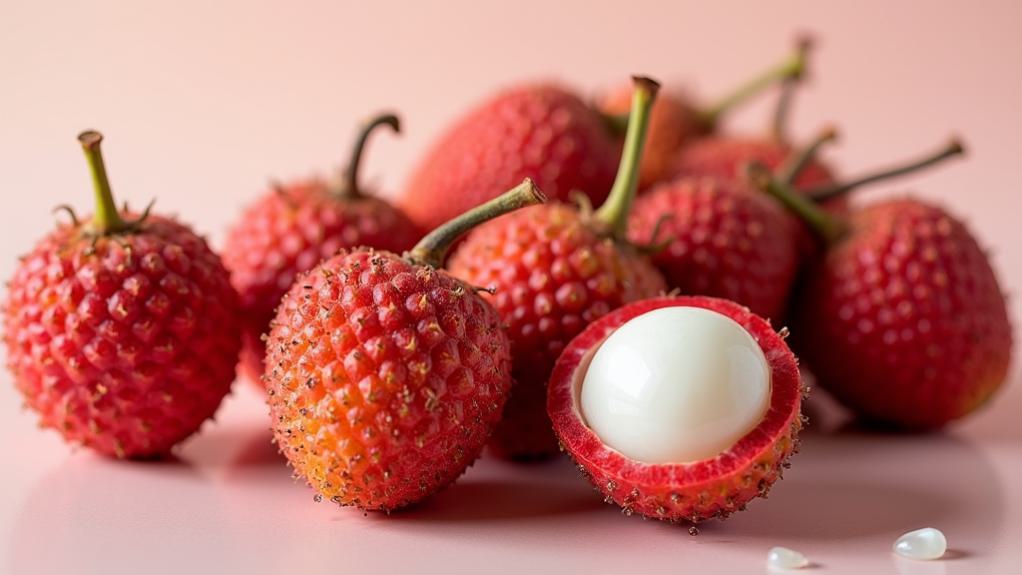

Lychee is a nutrient-rich fruit that may offer a variety of health benefits due to its impressive nutritional profile. A serving size of one cup (190 grams) contains approximately 125 calories, making it a low-calorie option for those seeking to maintain a healthy diet. The macronutrient composition is primarily carbohydrates, with about 36.7 grams per cup, derived mostly from natural sugars, totaling around 23.2 grams. The fruit is low in protein (1.6 grams) and fat (0.8 grams), making it a light and invigorating choice.
Lychee is also notable for its drinking water properties, consisting of approximately 82% water. Additionally, it provides a modest amount of dietary fiber, contributing 2.5 grams per cup, which may aid in digestive health.
The glycemic index of lychee is relatively low, meaning it may not cause significant spikes in blood sugar levels, contrasting favorably with processed sugars. For ideal health benefits, it is recommended to consume 10-12 lychees daily. However, this amount may vary by individual, so please consult with a doctor before making dietary changes.
Vitamins and Minerals
A 100-gram serving of lychee may provide 71.5 mg of vitamin C, fulfilling 119% of the daily recommended intake. This vitamin may be essential for immune system support, skin repair, and combating infections.
Additionally, lychee may contain several B vitamins, including thiamin, riboflavin, and niacin, which may play key roles in metabolizing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Lychee may be particularly rich in copper, with 437.0 μg per cup, representing 49% of the daily value. Copper may be important for red blood cell production and metabolic processes.
It may also provide a good source of manganese (627.0 μg per cup, or 27% of the daily value), which may be necessary for various bodily functions, including bone formation and detoxification.
Moreover, lychee may contribute potassium (345.8 mg per cup, 7% of the daily value), which may aid in heart health by regulating blood pressure. The presence of iron and zinc, albeit in smaller amounts, may further enhance its nutritional profile, making lychee an excellent addition to a balanced diet.
Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
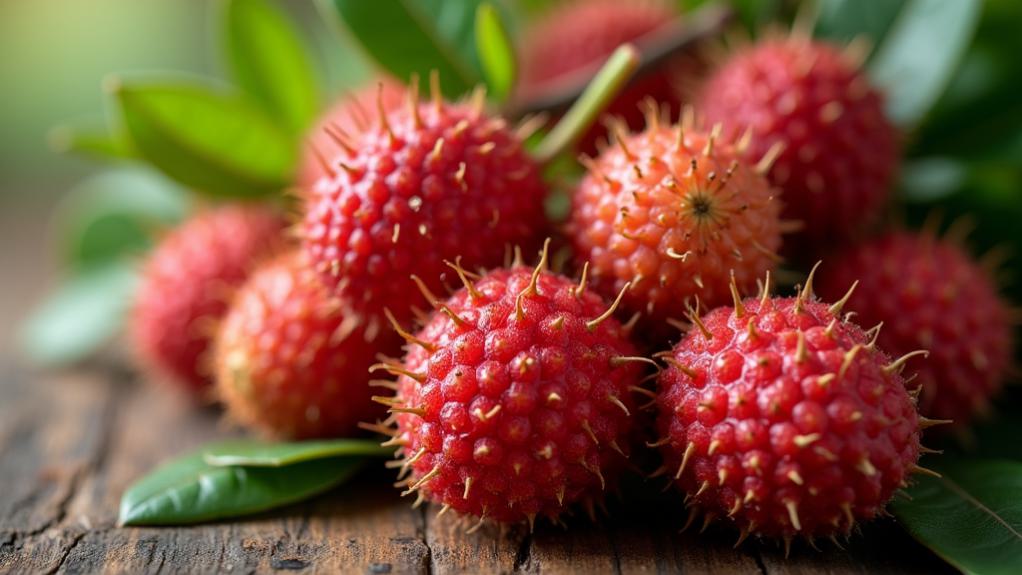

Lychee is exceptionally rich in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids and anthocyanins, which play an essential role in combating oxidative stress and promoting cellular health.
The fruit's high antioxidant content not only contributes to its cancer-fighting properties but also supports the prevention of various chronic diseases.
High Antioxidant Content
Lychee is packed with an impressive array of antioxidants that may benefit cellular health. This tropical fruit is particularly rich in polyphenols, providing an exceptional 492.4 mg per 240 ml serving. Other notable antioxidants include flavonoids—such as gallic acid and chrysanthemin—as well as anthocyanins and ascorbic acid, which may deliver 226% of the daily value of vitamin C.
The antioxidant functions of lychee may protect against damage from inflammation, stress, and environmental pollutants, while reducing oxidative stress and preventing free radical accumulation. This fruit may also support glucose and cholesterol metabolism, contributing to long-term health.
Here is a summary of the antioxidant composition in lychee:
| Type of Antioxidant | Amount per 240 ml Serving |
|---|---|
| Polyphenols | 492.4 mg |
| Carotenoids | 1085.7 µg |
| Ascorbic Acid | 226% of daily value |
Incorporating lychee into your diet may greatly boost immunity, maintain skin health, and aid in the prevention of chronic diseases, emphasizing its role in a balanced nutrition plan.
Cancer-Fighting Properties
Lychee may exhibit significant cancer-fighting properties due to its rich content of antioxidants and phytonutrients. Research indicates that lychee extracts may demonstrate reduced cell proliferation and induced cytotoxicity across various cancer cell lines. The constituents of lychee may promote autophagy through increased cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, effectively triggering proapoptotic, antiproliferative, and antimetastatic activities.
Particularly significant are the phytochemicals found in lychee seeds, which may be abundant in polyphenols like flavonoids and proanthocyanidines. These compounds may show strong antioxidant and anti-cancer activities, with specific flavonoid glycosides such as litchioside D and kaempferol 7-O-neohesperidoside displaying anti-neoplasm effects.
Studies have confirmed that lychee seed extracts may inhibit cell proliferation and induce cell-cycle arrest in colorectal cancer cells, impacting critical apoptotic pathways.
While in vivo studies may demonstrate promising results—such as significant reductions in tumor size and metastasis—further research, especially clinical trials, is essential to validate these findings for human cancer prevention and intervention.
The potential of lychee as a chemoprevention agent may warrant continued exploration in the field of oncology.
Health Benefits of Lychee
Lychee may offer a remarkable array of health benefits, primarily due to its rich nutritional profile. High in vitamin C, with 71.5 mg per 100-gram serving, lychee may bolster immune function and enhance the body's ability to fight infections. Additionally, lychee juice may possess probiotic benefits that can improve gut health and immune modulation.
Lychee may also provide strong antioxidant properties, containing polyphenols that protect cells from oxidative damage. Research indicates that its extracts may exhibit high radical-scavenging abilities, suggesting potential anti-cancer effects, although further studies are warranted.
Moreover, lychee may promote skin and liver health; vitamin C may aid in collagen production, supporting skin repair and anti-aging benefits. Early findings suggest lychee extracts may assist in liver function and detoxification processes.
From a cardiovascular perspective, lychees are low in calories and fat while providing essential minerals like potassium and copper, which may be crucial for heart health. Overall, the lychee fruit is a nutritious addition to a balanced diet, offering drinking water and a variety of health-promoting properties.
Safety and Potential Risks

Consuming lychee may pose safety risks, particularly if the fruit is unripe or if individuals have specific allergies. Unripe lychee may contain toxic compounds that can lead to hypoglycemic encephalopathy, especially in malnourished children. Symptoms may manifest rapidly, including headache, vomiting, and seizures, which can be mistaken for other conditions.
Additionally, allergic reactions to lychee may range from mild to severe, including anaphylaxis.
Key safety considerations include:
- Unripe Fruit: Avoid consuming immature lychee to prevent toxic reactions.
- Allergic Reactions: Be aware of potential allergies, which may lead to oral allergy syndrome or serious systemic responses.
- Geographical Risk: The highest risks may occur in regions with poor nutrition and rising lychee production, such as northern India and Bangladesh.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Rapid glucose screening may be essential for suspected cases of hypoglycemic encephalopathy, while severe allergic reactions may require immediate medical intervention.
Understanding these risks may help consumers make informed decisions about including lychee in their diets, ensuring safety while enjoying its unique flavor.
Tips for Incorporating Lychee
Lychee may enhance various dishes and beverages with its unique sweetness and juicy texture. Enjoy fresh lychees by peeling away the skin for a low-calorie snack or enhancing fruit salads with their distinct flavor.
For dessert, lychee may be incorporated into sorbets, ice creams, and puddings, providing a refreshing twist to traditional recipes.
In beverages, lychee may shine in smoothies and fresh juices. Blend it with other fruits for a nutritious drink or press it for standalone juice. For a creative touch, consider adding lychee to tea, infused water, or cocktails, where its sweetness may complement various spirits.
In savory applications, lychee's sweetness may pair well with salads, adding a tangy contrast. It may be included in Asian-inspired dishes like stir-fries or curries, or mixed into salsas and chutneys for a fruity kick.
Additionally, lychee may enhance savory sauces and marinades, creating a harmonious balance of flavors. By incorporating lychee into both sweet and savory dishes, you may elevate your culinary creations while enjoying its numerous health benefits.